GREASE THOSE WHEELS (ECONOMICS)
#3 UNEMPLOYMENT
- Employment Statistics
- Size and components of labour force
- Labour productivity
- Definition of unemployment
- Unemployment rate; patterns and trends in (un)employment
- Difficulties involved in measuring unemployment
Unemployment? We all are familiar with this word, living in today's world, but have you ever tried to get deeper into this stuff; like what causes it and what are its consequences. No? I was expecting that! So lets just explore this phenomenon which we hear about almost everyday!!
First of all we should know as to how we measure via the employment statistics the rate of unemployment in a country. Simple...
- The total civilian labour force (people who are aged 16 or above and are employed or actively searching for unemployment) is determined.
- Next the number of unemployed persons is determined (the people who are actively looking for jobs or have not worked for more than an hour in the week before the survey was conducted)
- Exclusion of people who are employed by the military, have a long term illness or are voluntarily unemployed.
- Unemployed Persons / Total Civilian Labour force x 100 = Unemployment Rate.
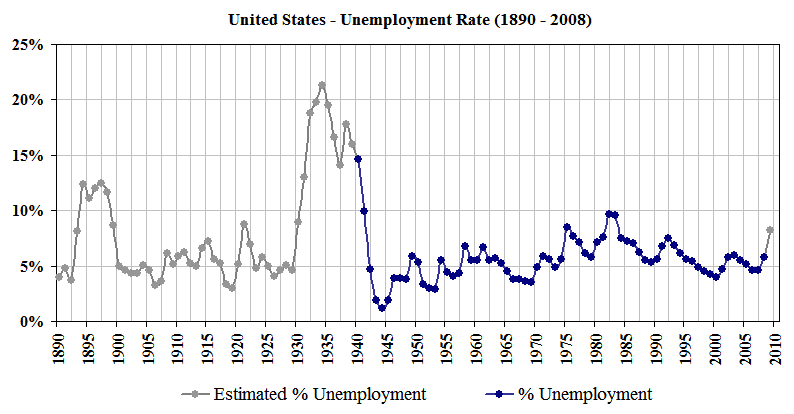
The above figure showing the unemployment rates of the U.S shows that unemployment is a dynamic concept and keeps on changing with time as more people come of working age and start finding jobs or get jobs along with other people who lose their jobs. So at a given time if more people get jobs and lesser people lose their jobs, the rate of unemployment will drop, and vice versa.
Some 'jumps' in the above graph are explained...
- 1929 and onwards was the Great Depression the period of great economics instability around the globe. Revenues dropped for firms and so they started striking off people from their factories.
- 1945 was the year when the U.S went all out in war against the Nazis, more of everything was required in the country, more ammunition, more food and more clothing. Thus as a result unemployment dropped (people became self employed as well) to an all time low as America coped with the war and the GNP almost doubled.
- 1970-71, 1974-75, 1980-81, 1983-84, 1991-92, 2003-04 were all recession years in the U.S economy.
- In 2008 another period of economic recession hit the world and unemployment is increasing and expected to increase.
Additionally unemployment is also very difficult to measure because...
- Data collection may not be accurate or may be subjected to mathematical errors or a wrong response from the people surveyed.
- Some people of working age may not prefer to work due to family business or other causes.
- Data collection is very time-consuming and expensive.
- People might disguise their unemployment.
- They dynamic nature of unemployment makes it difficult to keep track of so many changes.
- frictionally and casually unemployed portion of the labour force is difficult to measure.
Now let us look at the costs and effects of unemployment...
- Total economic output decreases, i.e the GDP, (as it is the next best alternative) as the available manpower decreases. It is known as the GDP gap and is shown as the distance between a point inside a PPF and a point on the PPF.
- Unemployed people's benefits also put an extra burden on the governement.
- Increase in the Misery Index which is also known as the discomfort index which is the sum of the rates of inflation and unemployment and depicts the suffering of an individual.
- The uncertainity that lurks when unemployment exists severely hinders economic growth, as worker insecure about their jobs do not make some buyings which results in decreased revenues for firms and thus they start increasing prises, contributing to inflation. Government also reduces spending on social welfare projects like construction of roads etc as it is unsure about the tax revenues it will get.
- Loss of revenue to the governemnt in the form of decreased income taxes and national insurance.
- Economic instability also contributes to the political instability of a nation. For example a government that has failed to cope with unemployment and other economics vices is tagged as useless and an average voter starts to look for changes. Bill Clinton's victory over George Bush in the 1992 elections is largely contributed to the recession of 1991.
- Loss of self confidence of the individual.
- Increased crime rates, family break-ups, suicides and other social vices.

Now let us look at the different sources of unemployment that exist on this planet of ours...=P
- Frictional Unemployment is caused by people quitting one job and looking for another one, in other words, when workers are between jobs. This is usually for a short period of times. As long as freedom of choice exists for workers, there always be some frictional unemployment.
- Structural Unemployment results from economic growth, changes in consumer tastes or any other factor that changes the way an economy operates and thus reduces the demand for some workers. It may also be due to outsourcing (the hiring of foreign firms to carry out not-that-important functions for a local company like customer support, availability of technical support, an example is the Hewlett-Packard Company. It is mostly done to lower operational costs). Some examples are...via economic growth; the advent of automobiles resulted in a decreased demand for horse-carriage makers and they went out of business due to structural unemployment, via changes in customer's tastes, popularity of Toyota automobiles resulted in structural unemployment in the U.S company, Ford, via the government, the 1990 closure of many military bases resulted in structural unemployment.
- Technological Unemployment occurs when simply put, machine take over the work from workers. Thus making the worker's skills obsolete. Since the advent of computers such unemployment had been steadily on the rise. Although some say it should be linked with the structural unemployment bu the magnitude of the two unemployments keep them apart with technological unemployment not on that large scale as structural unemployment goes on. Examples can be of proof-readers as spell-checking programs appeared, database managers as database managing programs appeared.
- Cyclical Unemployment is related to swings in the business cycle that forces firms to put off some workers until economic conditions improve, which is usually after several years. Economic instability such as recession usually results in millions of jobs being lost and is an example of cyclical unemployment.
- Seasonal Unemployment results from changes in demand for a specific type of workers at regular intervals or at fixed times every year. Example can be of crop-harvesters who are required in under-developed countries like India when the season of crop harvest arrives and are unemployed for most of the year.
- It is given by the formula Total Output/Total Employed Workers x 100.
- It is a measure of quantity of good produced by one worker in a firm.
- Here are some factors that affect labour productivity.
- Experience...the more the experience the more the productivity.
- Attitude towards the job...if it is loyal then increased productivity but if it is that of burden and half-heartedness then lesser the productivity.
- Wages; the lower the wages the lower the productivity and vice versa.
- Attitude of supervisor. It matters a lot if it is encouraging then good going, but when it gets overly bossy then......=P
- The use of newer technology.
- The facilities provided to workers.
Thats all from this topic....see you later with some other boring component of your syllabus...=PP


No comments:
Post a Comment